Machine Learning Algorithms in Python and R
This course has been designed by two professional Data Scientists who share their knowledge and help you to learn complex theory, algorithms and coding libraries in a simple way. It takes you step-by-step into the World of Machine Learning. With every tutorial you develop new skills and improve your understanding of this challenging yet lucrative sub-field of Data Science.
- Part 1 - Data Preprocessing
- Part 2 - Regression: Simple Linear Regression, Multiple Linear Regression, Polynomial Regression, SVR, Decision Tree Regression, Random Forest Regression
- Part 3 - Classification: Logistic Regression, K-NN, SVM, Kernel SVM, Naive Bayes, Decision Tree Classification, Random Forest Classification
- Part 4 - Clustering: K-Means, Hierarchical Clustering
- Part 5 - Association Rule Learning: Apriori, Eclat
- Part 6 - Reinforcement Learning: Upper Confidence Bound, Thompson Sampling
- Part 7 - Natural Language Processing: Bag-of-words model and algorithms for NLP
- Part 8 - Deep Learning: Artificial Neural Networks, Convolutional Neural Networks
- Part 9 - Dimensionality Reduction: PCA, LDA, Kernel PCA
- Part 10 - Model Selection & Boosting: k-fold Cross Validation, Parameter Tuning, Grid Search, XGBoost
Regression Modelling - Linear & Polynomial
In the first secgtion we look at the basics of Linear Regression Algorithms, Mutliple Linear regressions then moving onto Polynomial Linear Regression Modelling (Left to right)
In the examples below, I used various regression modelling techniques to solve different challenges. The process is geenrally similar throughout:
- Data Preprocessing: In order to do this I had to preprocess the data, remove anomalies, NaN values and any other bad data that could corrupt the data set. Also if required you need to Feature scale the data.
- Define the Independent variable(s) and Dependent Variable (the one you are trying to solve for)
- Data Split: I then split the data into training data and test data. Usually a 70/30 approx split Train:Test set.
- Build Regression Model: Run the regression model by calling the regressor Class on the training data and look to fit the curve function to the original Data set
- Predict the outcome: Then we use the ML algortihm prediction function to try and predict a plot that shows how our ML algorithm has correlated the importance of the independent variable(s) to the dependent variable
- Visualise Results: Using Matplotlib we then plot results and compare the predicted ML Model to the test data that the algorithm has not yet seen, and see how well our ML model has predicted the given result
In the two examples below, I used linear regression modelling to predict a Salary for a data scientist given the number of years of experience. On the right hand side I used a Polynomial Linear Regression model to predict a similar challenge of where a salary should sit relative to a given experience level. The challenge in this case was that as it was vertical progression within a company from intern to CEO the correlation was more exponential and therefore required a polynomial regression to better fit the curve.


Multiple Linear Regression Modelling
The Multiple Linear Regression model was slightly more complicated as the challenge here was to correlate the profitability of a portfolio of companies based on multiple variables like location, R&D spend, marketing spend and Administration spend.
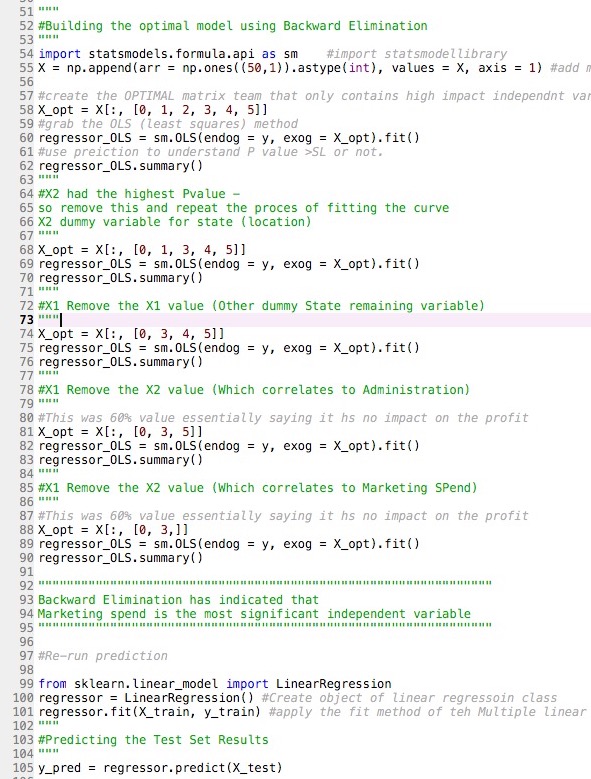
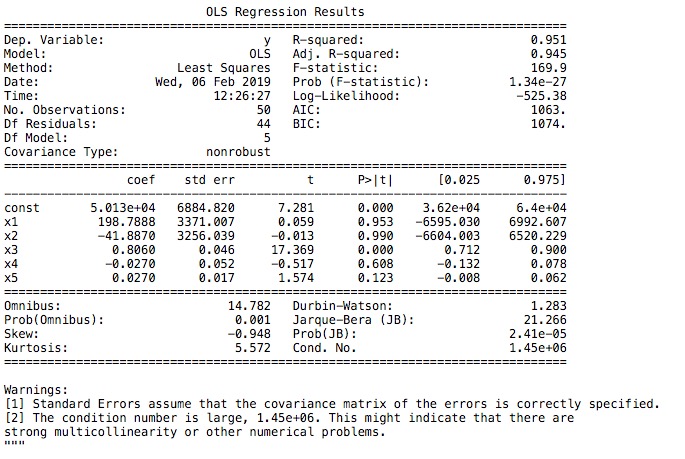
The aim is for a VC firm to be able to analyse their existing portfolio data and decide what metrics matter most when looking for new investment opportunities. By using multiple linear regression the ML algorithm can correlate multiple independent variables and see a) how statistically significant they are to the dependent variable – profit and b) how all of the independent variables work together to have an impact on the profit factor. In this multiple linear regression model I also used the backwards elimination process to sequentially remove any variables where the P-value was higher than the significance value which would indicate that the impact of the profitability was most likely negligible to the outcome.In the pictures below you can see the Python code for the backwards elimination process then also the outcome of the regression analysis using the least squares method (OLS)
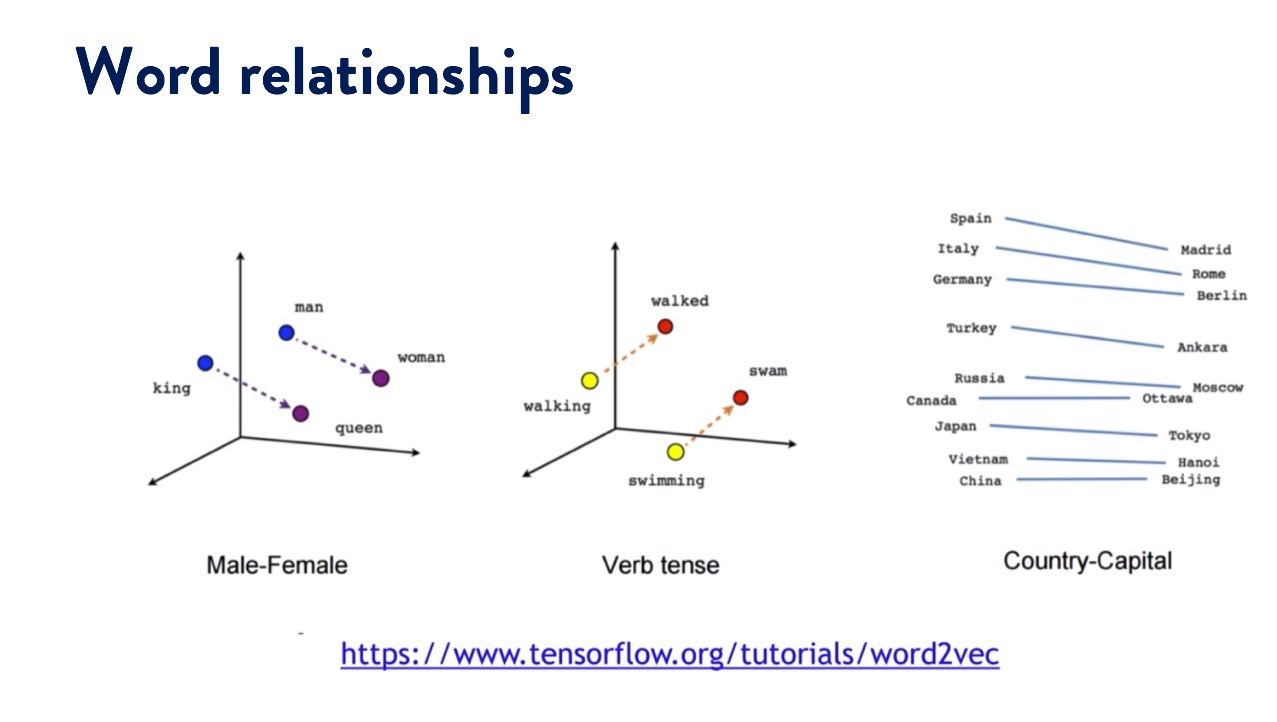
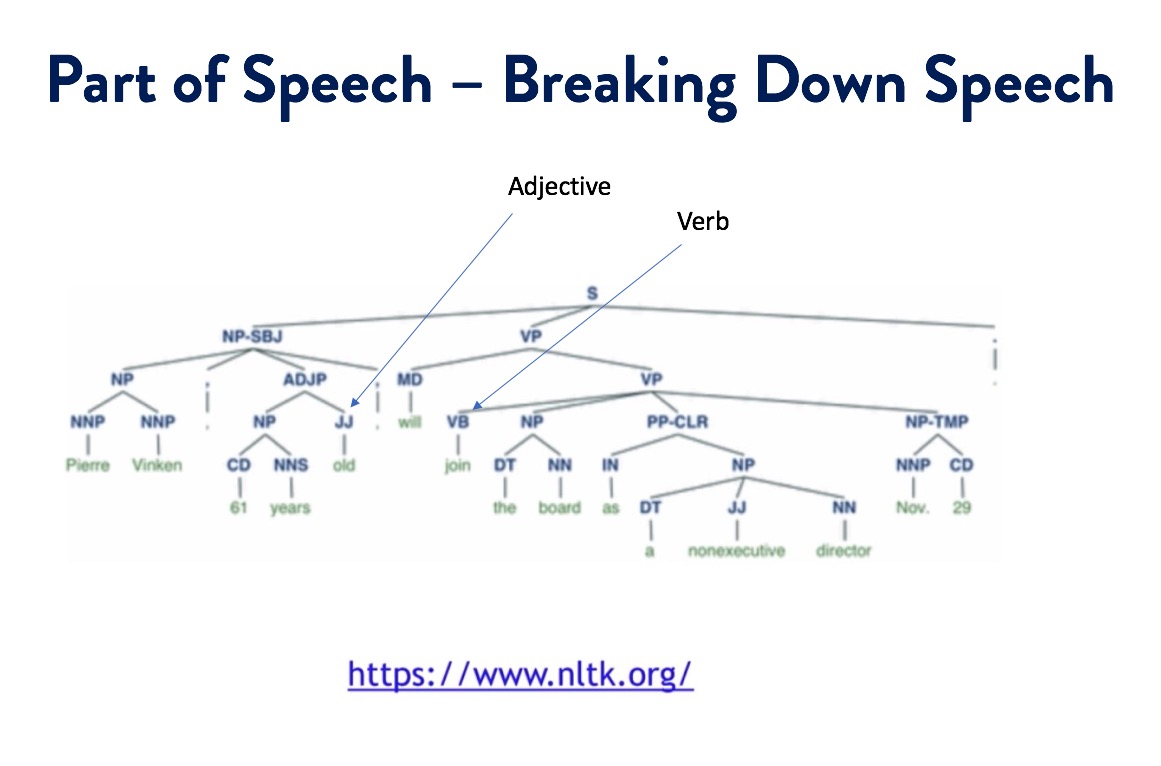
Natural Language Processing
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is an area of computer science and artificial intelligence concerned with the interactions between computers and human (natural) languages. NLP is used to apply machine Learning Models to text and Language. Examples of this would be teaching machines to understand what is said in spoken and written word (like Siri or Alexa).
In this exercise I used various Python plugins including NLTK (Natural Language Toolkit) and re (Regex) which is a regular expression plugin for pre-processing the text we want to analyse.
The objective was to take a set of 1000 restaurant reviews, in .tsv format and to analyse them with the ML model, in this case we used Naive Bayes model. Then to train the data to try and predict the outcome on the test set of whether or not the review was positive or negative based on the words it contained.
The final model actually predicted the outcome of the reviews to around 73% accuracy which I’m led to believe for a “small” training data set of 800 reviews; this is actually quite a good initial outcome! But with additional refinement and training this could obviously be improved.
The process here was quite simple, first we clean the data in order to reduce the number of words that will be used in our final matrix of independent variables.
- Import the .tsv file
- Clean the text file, make all lower case, remove punctuation etc.
- Split the sentence into an array
- Use the PorterStemmer method – this essentially reduced words for example “Loved” becomes “love”.
- Remove the stop words, i.e it, was, the
- Apply a filter to remove infrequently used words
- We then loop through the entire dataset running this model and re-append each review back into a string
Second, we use tokenization to assign each of the remaining independent variables into a very large matrix 1000 x 1500 with 1500 independent variable. Here the CountVectorizer method will assign a 1 if the word is present or a 0 if the word does not appear in the review.
We then split the data set into training and test data, and the Naïve Bayes machine learning algorithm will try to correlate the matrices of independent variables to the dependent variable y which is simply “good” or “bad” , a 1 or 0 review score.